Body Heat Is A By-product Of Cellular Metabolism. Environmentl Fctors Nd Performnce Ppt Downlod
The ability to produce heat from calories is. “what we’re really interested in is. Heat is both a byproduct of metabolism and a form of energy that influences the speed at which metabolism occurs, otherwise known as metabolic rate.
7a4 Metabolism HumanBio
Cellular level heat is generated on a cellular level by metabolism. However, all human populations, regardless of activity levels, spend similar amounts of energy for their body size on their resting metabolic rates. Most of the heat produced in the body is generated in the liver, brain, heart, and skeletal muscles during exercise.
Energy produced or consumed by a chemical reaction depends on the difference between the.
In all cells, glycolysis occurs in the cytosol and consists of the catabolism of glucose to produce two. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like by product of cell metabolism, means of conserving increasing body heat, means by which heat is distributed to all body. The metabolic rate, on the other hand, indicates how quickly the body converts food into energy, influenced by various factors including body composition, age, and activity level. Major metabolic pathways regulating cellular metabolism.
Mechanisms of heat production are metabolic chemical reactions that yield heat. This comprehensive article aims to explore the biochemistry of. Hyperthermia triggers inflammation, coagulation, and progressive multiorgan. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like production of heat is called, what is one way the body produces heat?, body heat is a by product of?

7a4 Metabolism HumanBio
The production of the metabolic heat is the reflection of the cellular life that results from the consumption of oxygen (o 2) and rejection of carbon dioxide (co 2).
In the process of atp production by cells throughout the body, approximately 60 percent of the energy produced is in the form of heat used to maintain body temperature. The basal metabolic rate increases by thyroid hormone, sympathetic stimulation, muscle activity, and chemical activity. Heat production is a function of metabolism. Humans are endotherms, animals that keep their body temperature within a stable range using heat production and heat dissipation.
Energy metabolism is indispensable for sustaining physiological functions in living organisms and assumes a pivotal role across physiological and pathological conditions. Heat represents the transfer of energy between molecules, while calories measure the energy content of food. Metabolic heat can be estimated based on actual measurement of oxygen consumption of a. The metabolic heat generated by a person increases as a function of the physical work performed.

Unit 8 Cellular Respiration and Energy Metabolism Douglas College
However, two tissues actively produce heat against cold, namely bat and skeletal muscles.
Metabolic heat production refers to the process by which organisms generate heat as a byproduct of metabolic activities, primarily during the conversion of food into energy. Mammal metabolism is intimately connected to the maintenance of body temperature.
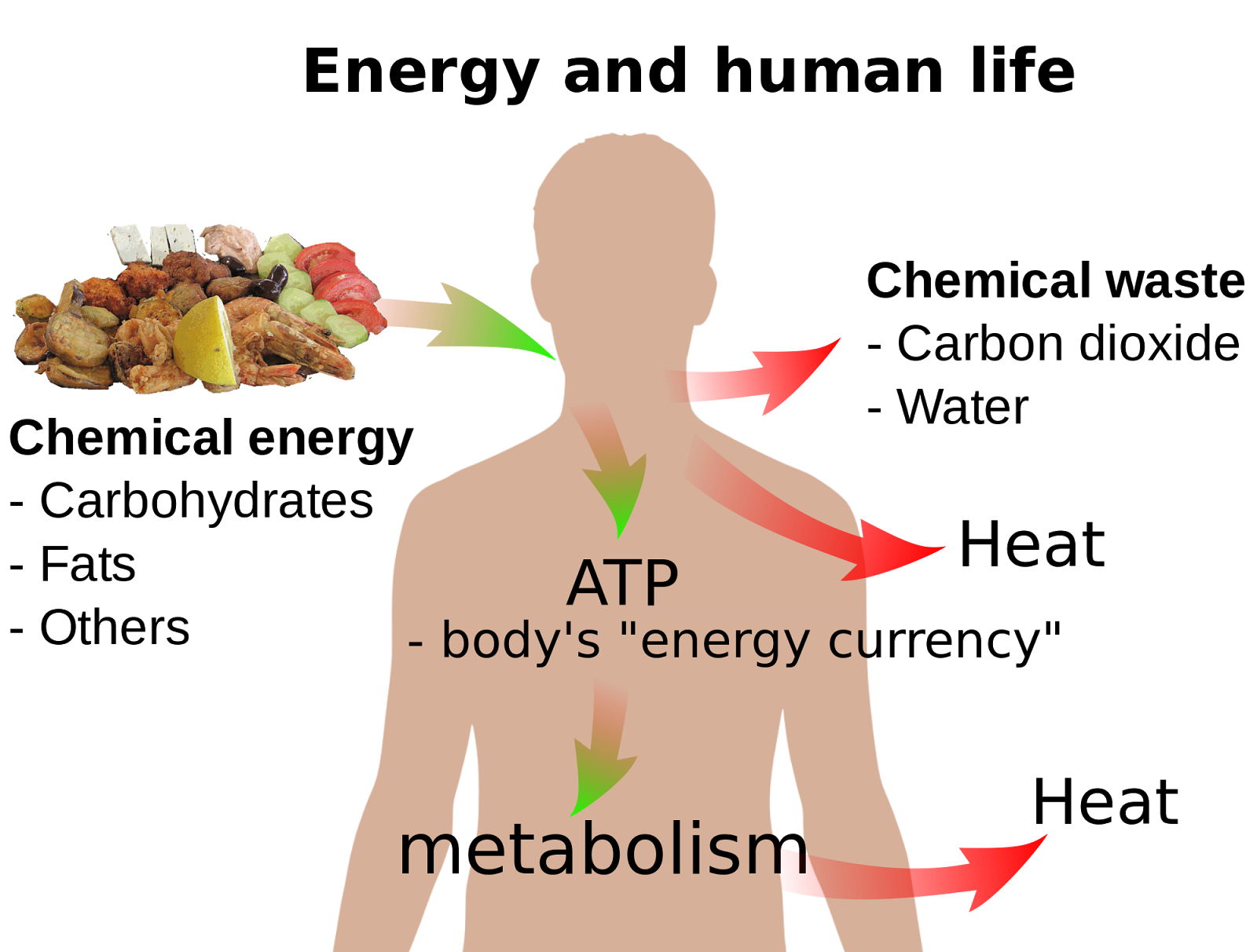
97 Summary of Energy and Respiration Biology Notes for A level

Environmental Factors and Performance ppt download