Viscosity Meaning A Deep Dive Into Fluid Dynamics Formul Mechnics Klopmint
Dynamic viscosity or absolute viscosity is the fluid’s resistance to motion when an external force is applied to shear the fluid. There are two ways to measure the fluid’s viscosity as follows: Dynamic viscosity is a measure of a fluid's internal resistance to flow, reflecting how thick or sticky a fluid is.
Low Viscosity Meaning Online Offers
Viscosity is the measure of a. When there is relative motion between layers of fluid, viscosity can be defined and measured. Dynamic viscosity is also known as absolute viscosity and is defined as the measure of a fluid’s internal resistance to flow or shear stress.
It explains newton’s law of viscosity, the equation that describes the linear relationship between the shear stress in a flowing fluid fluid and velocity gradient, the constant of proportionality between the two terms being the fluid.
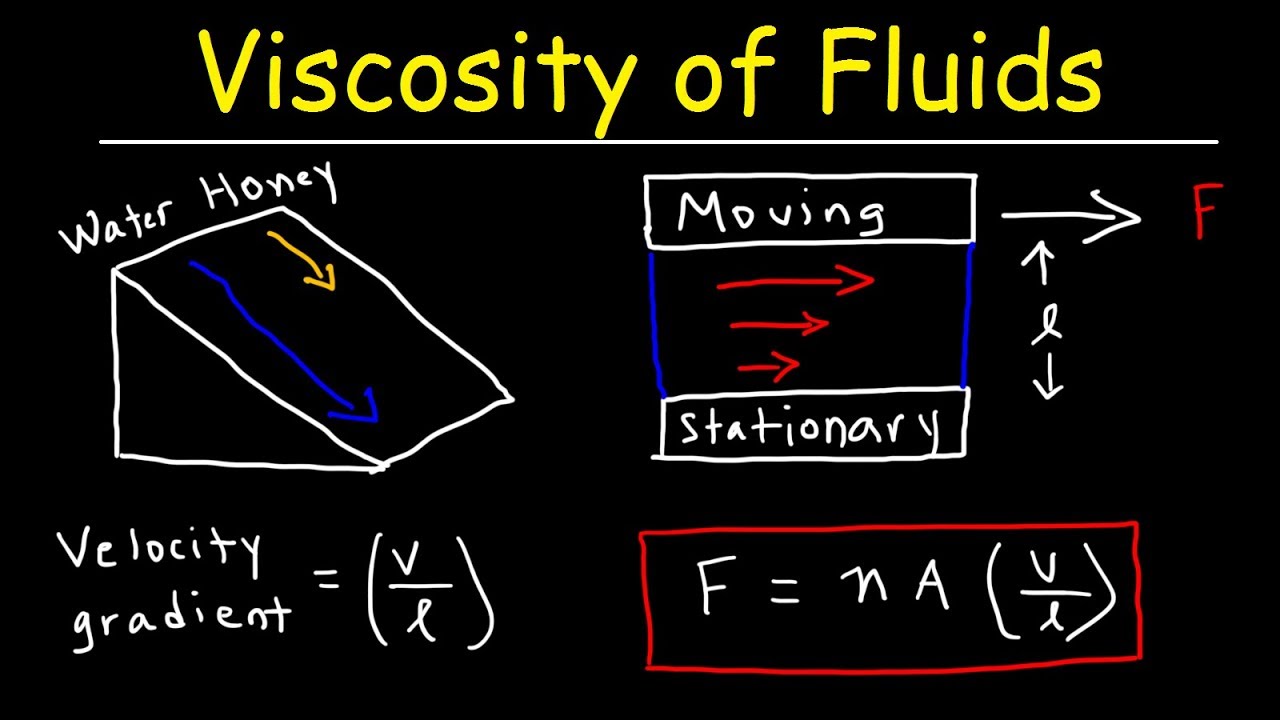
This characteristic of fluids delves into. Honey has high viscosity (pours slowly) and water has low viscosity (pours quickly). Viscosity is a fundamental property of fluids that significantly affects fluid dynamics and is a critical consideration in engineering design. Density is vital in fluid dynamics, lubrication, and industrial processes, while viscosity plays a crucial role in hydraulics, research, and quality control.
It quantifies the force needed to move one layer of fluid over another and is crucial. Dynamic viscosity, often denoted by the greek letter mu (μ), is the most. Informally, viscosity is the quantity that describes a fluid's resistance to flow. The viscosity of a fluid has an impact upon how that fluid may behave and interact with surrounding objects.

Mastering Fluid Dynamics Understanding Viscosity
Simply put, a fluid’s internal resistance to flow is called viscosity.
Role of viscosity in fluid mechanics. Kinematic viscosity is the resistive flow of fluid under the action of gravity. Understanding how viscosity influences fluid behavior is essential for engineers to ensure the. A higher kinematic viscosity indicates a thicker fluid that flows more slowly.
Viscosity is the measure of fluid’s friction to its flow. It's like the thickness of the fluid. Whether you’re a student diving into fluid dynamics or an engineer designing a system, this resource will help you understand this critical concept. It is expressed in units of poise.

Low Viscosity Meaning Online Offers
Dynamic viscosity and density are both crucial properties in fluid mechanics, and they serve different but.
Dynamic viscosity and kinematic viscosity. Formally, viscosity is the ratio of shearing stress to velocity gradient. Viscosity can be broadly categorized into two types: Dynamic viscosity takes into account the molecular interactions within a fluid, while kinematic viscosity considers the density of the fluid as well.
If a fluid is highly viscous, it is harder for an object to move through when. Kinematic viscosity is a critical aspect of fluid dynamics, offering insights into the fluid’s resistance to flow and its internal friction. Viscosity (also known as dynamic viscosity, absolute viscosity, or simple viscosity) is… represented by the greek letter η (eta) defined informally as the quantity that describes a.

Viscosity meaning science terystep
Viscosity formula fluid mechanics klopmint